In sheet metal fabrication laser cutting is a technology that uses a high-powered fibre laser beam to cut sheet metal with exceptional precision. Laser cutting works pretty much exactly as you’d expect, by using a computer numerical control (CNC) system to move the laser beam in a specific pattern, which melts the material and forms a cut.
If you’re familiar with sheet metal fabrication, you’ve probably heard of laser cutting. But you may not have heard of the unsung heroes of laser cutting: assist gasses.
In this article, we’ll talk about what assist gasses are, and how we use assist gasses to achieve unparalleled precision and finish quality for our laser cutting here at Ameritex.
What are Assist Gasses?
As the name implies, the term “assist gas” refers to the gas that is used in conjunction with a laser to make a cut. Assist gasses are distributed by a high-pressure nozzle that is located directly next to the laser beam. The pressure and flow rate of the assist gas can be adjusted depending on the needs of a specific cut.
The primary purpose of an assist gas is to remove molten material from the cut zone after it is melted by the laser. Using an assist gas prevents molten material from re-solidifying on the surface, resulting in a cleaner cut.
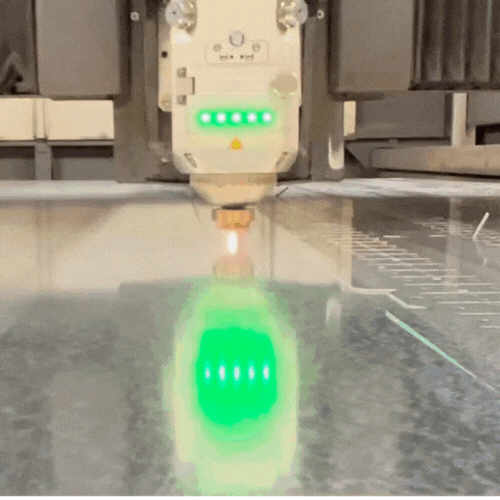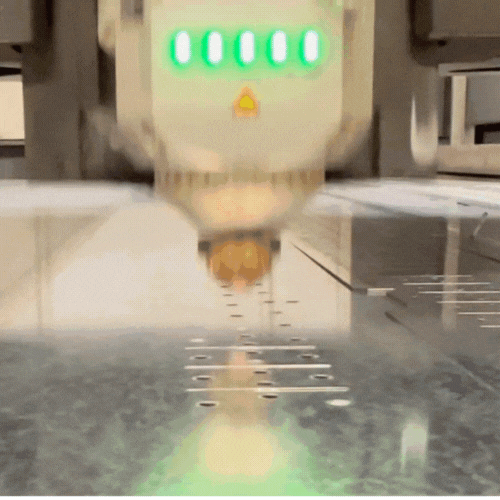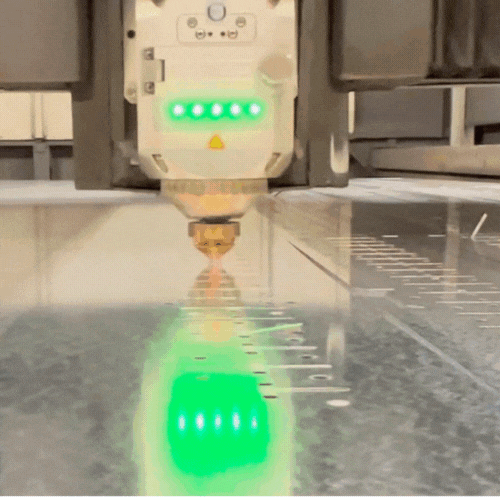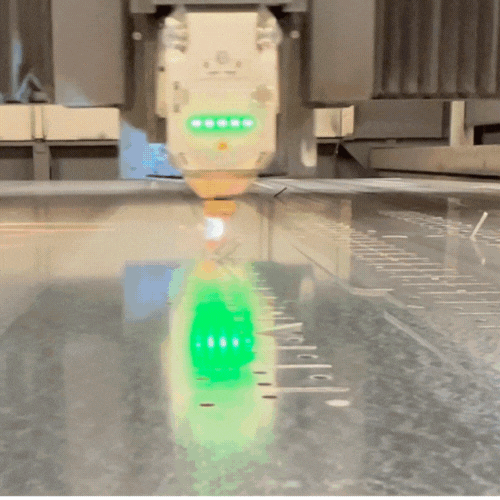
The Science and Art of Assist Gasses
There are a variety of different gasses that can be used as assist gasses in laser cutting, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are the three most popular:
- Oxygen: Oxygen is a reactive gas, and when used to laser cut certain materials like steel it can create an exothermic reaction that burns the material, facilitating the cutting process. Oxygen can also create an oxide surface with some materials, making it less desirable for some applications than other assist gasses.
- Nitrogen: Unlike oxygen, nitrogen is an inert gas that can help prevent oxidation during the cutting process. Nitrogen is also much faster to cut with than oxygen.
- Argon: Like nitrogen, argon is also an inert gas. Argon is more expensive than nitrogen, but it is also less reactive. As such, it is often used to cut metals that react with nitrogen, like titanium.
Choosing the right assist gas for a cut is both a science and an art. There are many factors to consider, such as the speed at which the material will be cut, the thickness of the material, the chemical reactivity of the material, the desired finish quality of the material, power required, and more.
For example, a thicker material will require a slower cut, so we are more likely to use oxygen. For thinner materials, we are more likely to use nitrogen – oxygen cuts at a higher temperature, which can warp thinner material. Copper, a unique material with specific manufacturing requirements, benefits from the use of oxygen, because the oxide layer formed during cutting reduces the reflectivity of the material, increasing the efficiency of the laser.
At Ameritex, we also use blends of different gasses to achieve exceptional results on our laser cut parts. A blend of 95% nitrogen and 5% oxygen, for example, can take advantage of the exothermic reaction created by oxygen, while maintaining the speed and clean finish provided by nitrogen. We are constantly refining our gas blends to create the perfect mixture for every application.
Your Trusted Laser Cutting Experts
At Ameritex, we are experts in custom metal fabrication. In addition to our laser cutting services and tube laser cutting services, we provide comprehensive metal fabrication services including tube bending, sheet metal forming, sheet metal assembly and finishing, and more. If you have a custom metal fabrication project in mind, request a quote today!